In the third part of our blog series “Intelligent Enterprise” we explain what conversational artificial intelligence (CAI) means, what benefits SAP’s bot platform offers and show practical examples in connection with SAP solutions and especially examples from the SAP S/4HANA environment.
Conversational AI with SAP S/4HANA (Part 3)

What is Conversational AI?
Current trends show that the time we spend using messaging apps like WhatsApp, Instagram Messenger, iMessage, Facebook Messenger, etc. will soon surpass face-to-face time. These messaging platforms have become increasingly sophisticated with features that go far beyond simply sending and receiving text messages. Many of them allow the sharing of photos, videos, documents and files, voice notes, location information, sports achievements, health status, etc. They create new opportunities for us to interact not only with each other, but also – thanks to chatbots – with machines, IT or ERP systems.
Communication via messaging apps is based on conversational AI technology, which is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) that lets users communicate with computers and machines in natural language. This involves providing a user interface (e.g. dialog box) or voice message recording software on the computer that imitates a conversation with a real human.
The possible uses of chatbots and voicebots are very diverse. They can be used both for communication with internal IT systems (i.e. for the company’s own employees) and for communication with external business partners (i.e. with customers and suppliers).
SAP Conversational AI
SAP has developed SAP Conversational AI (SAP CAI) as an end-to-end enterprise chatbot platform. On this platform, intelligent AI-driven chatbots can be created, trained, and monitored in a single interface to simplify business tasks and workflows across SAP and non-SAP products and improve the customer experience. The platform supports a low-code development approach and provides user-friendly interfaces for both business power users and developers.
In my view, one of the main advantages of SAP CAI is the possibility to include the business process context in the chat. This can be, for example, SAP data objects, such as sales order number, purchase order number, etc., that the bot found in response to the user question. The user can click on these document numbers in the chat window and jump directly to the corresponding document.
In addition, the following features are available on the SAP CAI platform: Organizational unit and account management, versioning and update management, extensibility, bot training and usage statistics.
SAP has not yet delivered CAI best practices or preconfigured packages, but in the SAP CAI community you can find project templates for some business scenarios that a development team can use as a basis.
NTT DATA Business Solutions is also very active in the SAP CAI environment and has already successfully implemented a number of projects for customers and as part of SAP CAI hackathons as well as developed its own project accelerators and various templates. The connection of the chatbots with SAP S/4HANA was realized via various channels: Chat window directly in SAP S/4HANA, mobile app, MS Teams or via the website.
In the following, I describe some realized projects and explain how you can increase the attractiveness of operating your SAP solutions with SAP CAI.
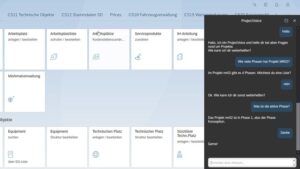
Chatting with SAP S/4HANA Project Management
This use case is about a chatbot that is connected to SAP S/4HANA Project Management. This chatbot enables the management and control of SAP PPM projects, and communication with the SAP S/4HANA system can also take place with the help of a voice assistant. The bot accesses an SAP backend in the background and can both read and write the data.
The bot can be used to query general information about projects as well as project-specific data, e.g. who is the project manager of project X? When are the start and end dates? What are the next milestones and which of them are critical? On the other hand, the bot can also perform actions and change data in the project, e.g. change status or enter a new person in charge.
The chatbot relieves the project managers and the project management office from answering standard questions and thus helps to reduce internal administrative costs.
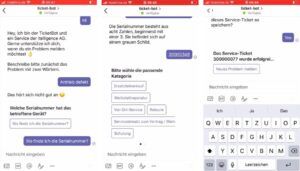
Create Service Tickets via Bot in SAP S/4HANA Service
In the next example, a bot relieves helpdesk or service staff when processing standard inquiries or answering frequently asked questions. The users are guided through the creation of a service ticket, which is saved in the SAP backend (here SAP S/4HANA Service) at the end of the conversation. The bot queries all the necessary information and saves it in a corresponding SAP backend transaction as a service ticket or message.
The integration of the service ticket bot can be realized via various communication channels and instant messengers, e.g. Microsoft Teams, WhatsApp, etc.
The use of such bots in customer service helps to automatically classify and pre-record a large part of standard requests and assign them to the appropriate processing groups.
Chatbot for a Supplier Self-Service with SAP S/4HANA Procurement
Purchasing or accounts payable typically receives multiple inquiries from vendors regarding the payment status of unpaid invoices. Responding to such inquiries is labor intensive, as the accounts payable clerk must navigate the system and send an email to the supplier for each invoice. This use case is about using a chatbot to enable the supplier to inform themselves about certain business transactions.
After briefly identifying the supplier in the chat and selecting the support category, the supplier’s employee types in one or more purchase order or invoice numbers and immediately receives the requested information about their business transactions.
The solution automates the response to standard requests, reducing the amount of work required to respond to suppliers.
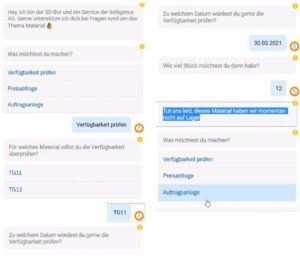
SAP S/4HANA Sales Bot Answers Customer’s Questions about Product Prices and Availability
A case study from the Sales & Service area: The idea is that customers who frequently ask about material price and availability can also direct their inquiries to a bot. The bot asks for the material name or number, the quantity requested, and the delivery date. If the material is available and the price can be accepted, there is also the option to order the material directly.
This example shows how your office staff can be relieved of simple standard queries and can currently devote their time to complex issues or customer support.
Chatbot for Employee Onboarding in SAP SuccessFactors
NTT DATA Business Solutions has implemented a chatbot solution in the area of employee onboarding that relieves the areas involved in the process of routine tasks. In this case study, the chatbot is used in combination with another software bot to start actions or further software applications from the chat dialog.
The HR employee starts the dialog by asking which employees are hired. The chatbot lists the names of the new employees. The next step is for the HR employee to select the person(s) to conduct the onboarding interviews. This first jumps to the scheduling screen to schedule employee interviews. In the next step, the bot jumps to the SAP SuccessFactors application to download the documents required for the employee interviews. The bot then triggers the ordering of the necessary hardware to equip the employee workstation and informs colleagues from purchasing via email.
With this solution, an HR employee can trigger the onboarding workflow through a single iteration with a chatbot agent, equipping both process participants and new employees with everything necessary and essential.
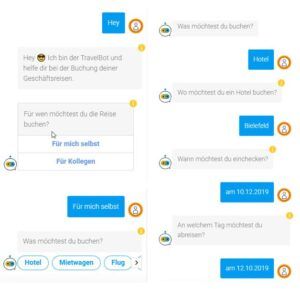
Chatbot for Travel Management in SAP SuccessFactors
In this case study, employees are supported by the chatbot to plan or book a business trip. At the beginning of the dialog, the user is asked whether he wants to book the trip for himself or for a colleague. Then comes the question about the desired category: rental car, plane, train or hotel. This is followed by detailed questions about the date, time, destination and a cost center or project number for cost allocation. Finally, the data entered is summarized by the chatbot and displayed again. After confirmation by the user, the travel request is sent to the travel management department.
The chatbot solution described above reduces the internal effort required to enter travel requests, relieves travel management staff of the burden of answering standard questions, and thus helps to increase productivity.
Are You Interested in Knowing More?
- Part 1: Your Path to the Intelligent Enterprise: Intelligent Technologies in SAP S/4HANA
- Part 2: Intelligent Technologies as Integral Part of SAP S/4HANA
- Part 3: Conversational AI: Chatting and Speaking with the SAP S/4HANA System
- Part 4: Machine Learning: Predicting Delivery Date Delays in SAP S/4HANA with Embedded AI
- Part 5: Software Robots Relieve Your Customer Inquiry Management – How RPA Works